The goal of knee replacement surgery is to decrease pain and restore function. Patients with osteoarthritis that is limited to just one part of the knee may be candidates for unicompartmental knee replacement (also called a "partial" knee replacement).
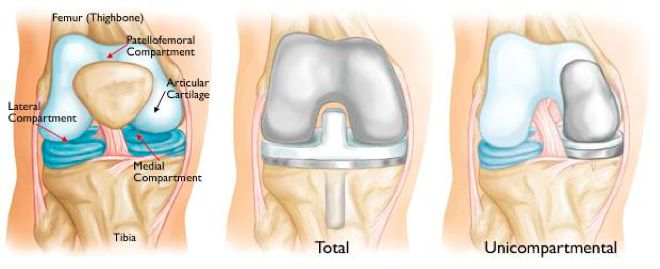
Your knee is divided into three major compartments: The medial compartment (the inside part of the knee), the lateral compartment (the outside part), and the patellofemoral compartment (the front of the knee between the kneecap and thighbone).
Unicompartmental knee replacement (also called "arthroplasty") is an option for a small percentage of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. Your doctor may recommend partial knee replacement if your arthritis is confined to a single part (compartment) of your knee. In a unicompartmental knee replacement, only the damaged compartment is replaced with metal and plastic. The healthy cartilage and bone in the rest of the knee is left alone.
Multiple studies have shown that modern unicompartmental knee replacement performs very well in the vast majority of patients who are appropriate candidates.
The advantages of partial knee replacement over total knee replacement include:
Also, because the bone, cartilage, and ligaments in the healthy parts of the knee are kept, most patients report that a unicompartmental knee replacement feels more "natural" than a total knee replacement. A unicompartmental knee may also bend better.
Your doctor may recommend surgery if you have more advanced osteoarthritis and have exhausted the nonsurgical treatment options. Surgery should only be considered if your knee is significantly affecting the quality of your life and interfering with your normal activities.
In order to be a candidate for this procedure, your arthritis must be limited to one compartment of your knee. Patients with inflammatory arthritis, significant stiffness, or ligament damage may not be ideal candidates. Your surgeon will help you determine if this procedure is suited for you. With proper patient selection, modern unicompartmental knee replacements have demonstrated excellent results in both younger and older patients.
A partial knee replacement operation typically lasts between 1 and 2 hours.
After the surgery you will be taken to the recovery room, where you will be closely monitored by nurses as you recover from the anesthesia. You will then be taken to your hospital room.
Because a partial knee replacement is done through a smaller, less invasive incision, hospitalization is shorter, and rehabilitation and return to normal activities is faster.
Patients usually experience less postoperative pain, less swelling, and have easier rehabilitation than patients undergoing total knee replacement. In most cases, patients go home 1 to 2 days after the operation.
You will begin putting weight on your knee immediately after surgery. You may need a walker, cane, or crutches for the first several days or weeks until you become comfortable enough to walk without assistance.
A physical therapist will give you exercises to help maintain your range of motion and restore your strength. You will most likely resume your regular activities of daily living by 6 weeks after surgery.
For additional information about this procedure, we have included this complete patient eduction sheet as a pdf to view, download and print: